
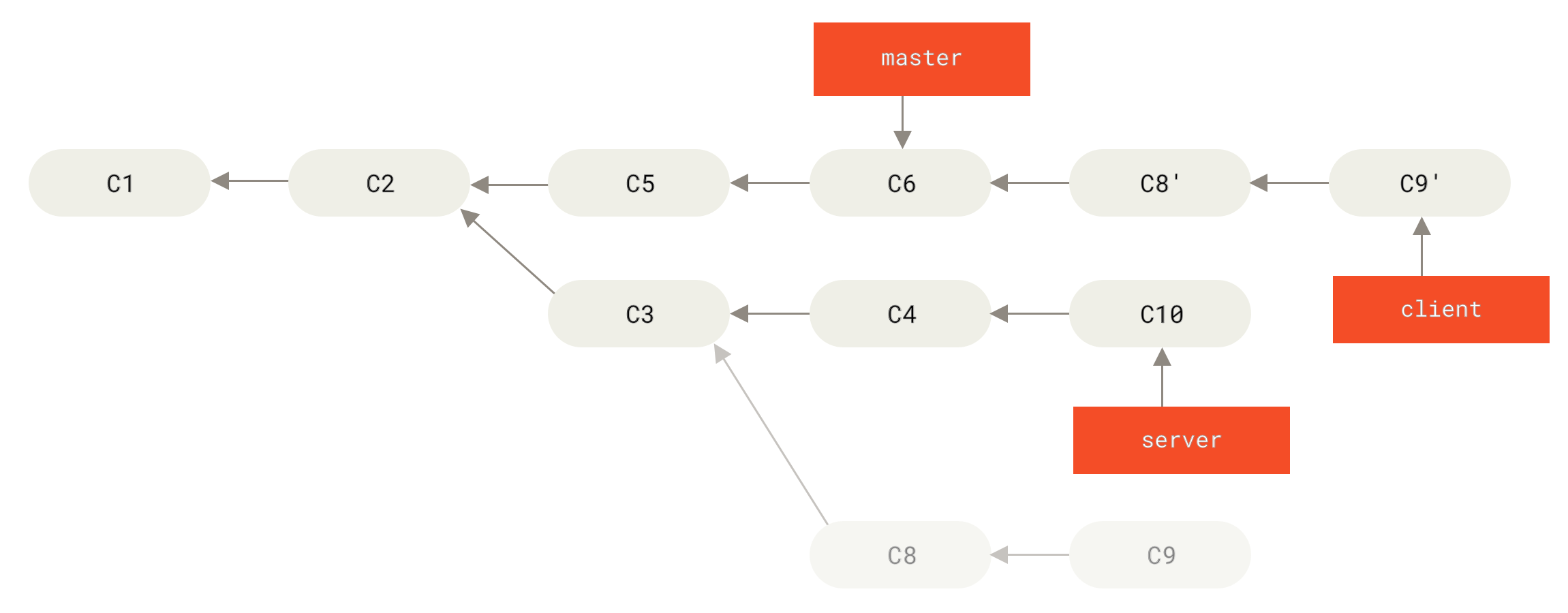
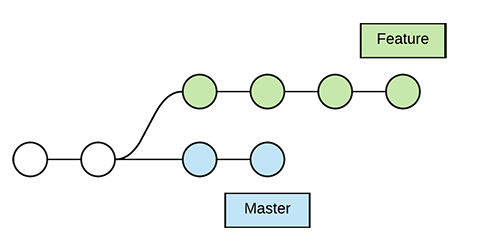
Use it with caution and make sure you understand the implications before applying it to your projects. Rebasing is a powerful technique, but it can be complex and risky.If you accidentally push the wrong branch, use the git reflog command to find the previous state and reset the branch.If you are unsure about the rebase process and want to practice, create a copy of your branch and rebase the copy instead.If you want to abort the rebase process, use the git rebase -abort command.Note: Use -force-with-lease instead of -force to avoid accidentally overwriting someone else's changes. Push the rebased branchįinally, push the rebased branch to the remote repository: git push -force-with-lease origin feature-branch Git will now finish applying the remaining commits. Once all conflicts are resolved, continue the rebase process with the git rebase -continue command: git rebase -continue Edit the files to resolve the conflicts, and then stage the changes: git add path/to/conflicted-file 4. Open the affected files in your text editor, and look for the conflict markers ( >). If there are any conflicts during the rebase process, Git will pause the operation and ask you to resolve them. This command will apply the changes from the feature-branch onto the main branch. Now, start the rebase process by using the git rebase command followed by the branch you want to rebase onto: git rebase main Next, switch to the branch you want to rebase: git checkout feature-branch To do this, use the git fetch command: git fetch origin 2. Fetch the latest changesįirst, make sure your local repository is up-to-date with the remote repository. Note: Rebasing can be a complex operation, and it is not recommended for beginners or when working on public branches, as it can cause confusion and conflicts. This results in a linear and more readable history. Instead of merging, which creates a new commit that combines the changes from two branches, rebasing rewrites the commit history by applying the changes from one branch onto another. Rebasing is the process of moving or combining a sequence of commits to a new base commit. It can help maintain a clean and linear project history, making it easier to understand and navigate. Rebasing is a powerful Git technique that allows you to integrate changes from one branch into another.
#Git rebase on another branch how to
Merging another branch into your project branchĬlick Choose a branch to merge into BRANCH.Ĭlick the branch you want to merge into the current branch, then click Merge BRANCH into BRANCH.In this guide, you will learn how to rebase a Git branch. For more information, see " Addressing merge conflicts."
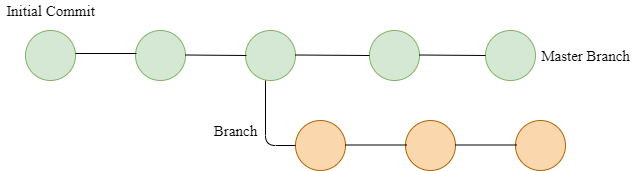 Resolve any merge conflicts in your preferred way, using a text editor, the command line, or another tool. git rebase
Resolve any merge conflicts in your preferred way, using a text editor, the command line, or another tool. git rebase To pull any commits from the remote branch, click Pull origin or Pull origin with rebase. To check for commits on the remote branch, click Fetch origin In GitHub Desktop, use the Current Branch drop-down, and select the local branch you want to update. For more information, see " About Git rebase" and " Rebasing your project branch onto another branch." Pulling to your local branch from the remote By rebasing you can reorder, edit, or squash commits together. Some workflows require or benefit from rebasing instead of merging. For more information, see " Merging another branch into your project branch" and " About pull requests." To request that changes from your branch are merged into another branch, in the same repository or in another repository in the network, you can create a pull request on GitHub Desktop. To apply changes to your branch from another branch in the same repository, you can merge the other branch into your branch on GitHub Desktop. To add changes from one branch to another branch, you can merge the branches. For more information, see " Pushing changes to GitHub from GitHub Desktop."
#Git rebase on another branch update
To update your branch on GitHub, you must push your changes. When you pull to your local branch, you only update your local copy of the repository. If you make commits from another device or if multiple people contribute to a project, you will need to sync your local branch to keep the branch updated. You can sync your local branch with the remote repository by pulling any commits that have been added to the branch on GitHub since the last time you synced.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
